Port Infrastructure and its Impact on Ship Turnaround Time

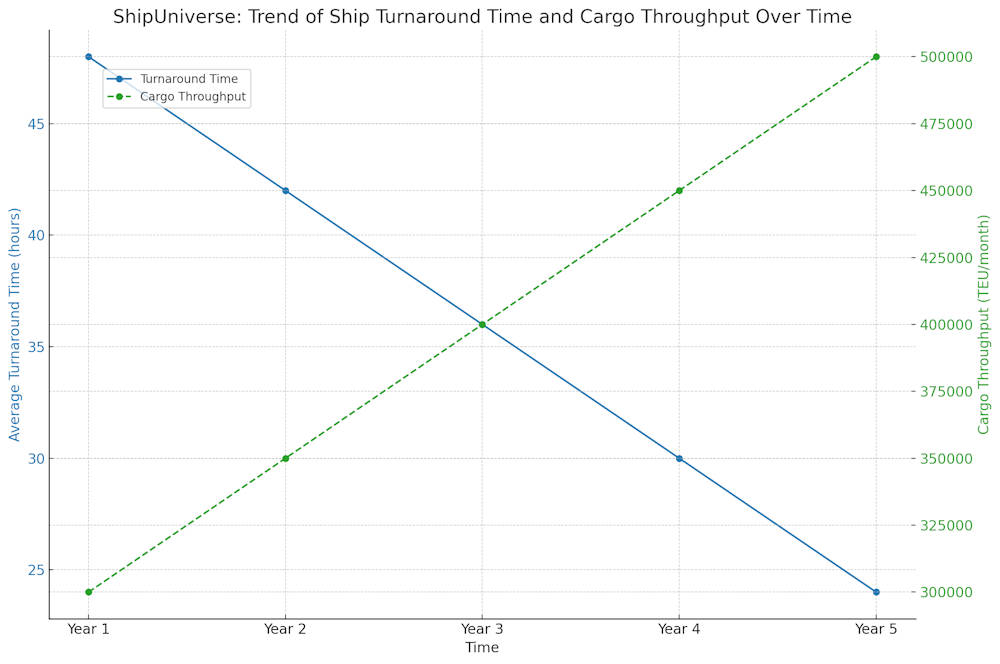
Ship turnaround time refers to the period a ship spends at port, from its arrival to departure. This measure is crucial because it influences the ship’s schedule, operational costs, and overall efficiency of maritime transport. Quick turnaround times are essential for decreasing port congestion, lowering docking fees, and enhancing cargo throughput, which collectively improve the profitability and competitiveness of shipping operations.
* Please send feedback/suggestions to editor @ shipuniverse.com
Factors Influencing Ship Turnaround Time
- Port Infrastructure: The layout and facilities of a port are fundamental. Well-equipped ports with up-to-date cranes, adequate docking space, and efficient storage solutions can significantly reduce the time ships spend at port. Efficient infrastructure ensures that loading, unloading, and servicing of ships are conducted swiftly and smoothly.
- Workforce and Management: The effectiveness of the port staff and the operational strategies they employ directly affect turnaround times. A well-coordinated team that operates seamlessly can dramatically reduce delays and streamline the entire process.
- Technological Advancements: Modern technology plays a critical role in optimizing port operations. Automated systems, real-time tracking, and digital documentation can expedite various processes, from cargo handling to customs clearance, reducing time-consuming manual tasks.
- Type of Cargo: The nature of the cargo also impacts turnaround time. Bulk cargo might require more time to load and unload compared to containerized cargo, which is generally quicker to handle due to standardized sizes and handling methods.
- External Factors: Various external conditions, such as weather, maritime traffic, and regulatory checks, can also influence the time a ship spends in port. Efficient ports anticipate and manage these factors through proactive planning and adaptive operational tactics.
Role of Port Infrastructure in Reducing Turnaround Time
Key Components of Port Infrastructure That Impact Turnaround Time
- Berthing Facilities: The availability and efficiency of docking spaces largely determine how quickly a ship can start its unloading and loading processes. Multiple or specialized berths can significantly speed up these operations, especially for larger ships or those requiring specific handling.
- Cargo Handling Equipment: Advanced cranes and handling equipment such as Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and gantry cranes ensure rapid movement of cargo between the ship and the port. Efficient cargo handling reduces delays and minimizes the time ships spend docked.
- Intermodal Transport Connections: Effective transport links for moving goods away from the port area—like rail, road, and further shipping options—are crucial. Well-integrated transport systems allow for quick transfer of cargo, preventing bottlenecks within the port.
- Technological Systems: Technologies such as Terminal Operating Systems (TOS) and Port Community Systems (PCS) help in managing the flow of information and cargo efficiently. These systems coordinate operations across the port, from berthing to logistics and customs clearance.
Examples of Infrastructure Advancements and Their Direct Benefits
- Automated Container Terminals: Ports like the Port of Rotterdam and Singapore have implemented fully automated container terminals where robots and automated cranes handle the loading and unloading of containers. These advancements have led to a reduction in turnaround times by minimizing human error and speeding up cargo handling.
- Smart Gate Solutions: Implementing smart gates at port entrances and exits facilitates faster and more secure processing of cargo trucks. For example, the use of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technologies allows for quick verification and clearance, reducing idle times for trucks.
- Enhanced Berth Scheduling: Advanced berth scheduling systems use AI to optimize the docking and departure times based on the cargo and ship specifications. This technology ensures that berths are promptly available when ships arrive, minimizing waiting times.
- Expansion of Berthing Options: Ports expanding their berthing facilities to accommodate more ships simultaneously or to host newer, larger vessel types directly reduce potential waiting times for docking space, thereby enhancing overall efficiency.
Technological Innovations in Ports
Introduction to Technologies that Streamline Operations
Technological advancements have significantly transformed port operations, making them more efficient and reducing ship turnaround times. Here are some key technologies:
- Automated Container Systems: These systems utilize robots and automated vehicles to handle container loading and unloading. By automating these processes, ports can operate continuously and more predictably, with less downtime and human error.
- Digital Communication Tools: Technologies such as real-time data exchange systems and cloud-based communication platforms enhance coordination between ships, port authorities, and ground staff. This ensures that everyone involved is on the same page, reducing delays caused by miscommunication or waiting for information.
- Port Management Software: Advanced software solutions integrate various operations within a port, from cargo handling to berth management and customs clearance. These systems streamline processes and provide actionable insights to improve efficiency.
- IoT and Sensor Technology: Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensors collect and transmit data from various points around the port, such as containers, trucks, and cranes. This data is used to monitor operations, predict equipment maintenance, and optimize cargo flows.
Case Studies Showcasing Successful Technology Implementation in Ports
- Port of Hamburg: Known as a “smart port,” Hamburg has implemented a range of digital tools, including IoT and big data analytics, to manage traffic and logistics more efficiently. These technologies help predict and manage cargo volumes and vessel traffic, significantly reducing waiting times and improving cargo handling speeds.
- Port of Los Angeles: As one of the busiest ports in the United States, the Port of Los Angeles has adopted an extensive Port Information Portal that allows shippers and carriers to view real-time data on cargo status. This system has improved the flow of goods, decreased truck idle times, and streamlined overall port operations.
- Port of Singapore: Continuously ranked as one of the most technologically advanced ports, Singapore uses automated quay cranes and driverless trucks at its terminals. These innovations have not only increased the port’s handling capacity but also drastically cut down the time ships spend in port.
- DP World, Dubai: This port has embraced hyperloop technology for cargo operations, aiming to create one of the most efficient and futuristic cargo handling operations. This technology is expected to revolutionize cargo movement with high-speed, low-friction transport tubes capable of moving goods inland rapidly and efficiently.
Impact of Efficient Port Operations on Maritime Logistics
How Reduced Turnaround Times Enhance Overall Supply Chain Efficiency
Reduced ship turnaround times at ports can have a profound impact on the entire supply chain, enhancing its overall efficiency in several ways:
- Improved Scheduling and Reliability: Faster turnaround times enable more predictable scheduling. Ships that spend less time in port can adhere to tighter schedules, which increases reliability in the delivery timelines throughout the supply chain.
- Increased Cargo Throughput: Efficiency in port operations allows more cargo to be handled in less time. This means ships can carry more loads in and out, increasing the total volume of goods moved and decreasing the cost per unit transported.
- Reduced Inventory Costs: With ships moving faster and cargo being processed more quickly, companies can reduce the amount of inventory they need to keep on hand. This just-in-time delivery model minimizes warehousing costs and reduces capital tied up in stock.
- Enhanced Supply Chain Flexibility: Efficient ports act as agile nodes in the supply chain network. They can quickly adapt to changes in cargo volume or destinations, thereby supporting more flexible and responsive supply chain strategies.
Economic Benefits for Shipping Companies and Ports
The economic advantages of efficient port operations extend to both shipping companies and the ports themselves:
- Lower Operational Costs for Shipping Companies: Quicker turnaround times mean ships spend less time idling at ports, which reduces port fees, labor costs, and fuel consumption associated with running auxiliary ship systems. This overall reduction in operational costs can significantly enhance the profitability of shipping operations.
- Increased Port Revenue: Efficient ports can handle more vessels and more cargo, leading to increased revenue from port services. As a port becomes known for its efficiency, it attracts more business, which can lead to further investments and improvements.
- Attractiveness to Global Trade: Ports that are known for their efficiency become preferred hubs within global shipping networks. This not only increases direct traffic but also boosts the local economy by supporting industries related to shipping, logistics, and trade.
- Sustainability Gains: Efficient operations often go hand-in-hand with sustainable practices, such as reduced fuel use and decreased emissions, both from ships and port equipment. This can lead to cost savings in terms of energy consumption and compliance with increasingly strict environmental regulations.
Challenges and Considerations
Common Challenges in Upgrading Port Infrastructure
Upgrading port infrastructure involves several challenges that can complicate the process:
- Financial Constraints: Significant investments are required to modernize port facilities and implement advanced technologies. Ports may struggle to secure funding, especially in regions where economic conditions are challenging or where ports are not prioritized in national budgets.
- Logistical Complexities: Overhauling existing infrastructure often requires ports to remain operational during upgrades. Managing construction and modernization without disrupting ongoing operations demands meticulous planning and can lead to temporary inefficiencies.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Ports operate under a complex web of local, national, and international regulations. Changes in infrastructure or operations must comply with all relevant laws, which can vary widely by jurisdiction and involve lengthy approval processes.
- Technical Integration: Integrating new technologies with existing systems poses significant technical challenges. Ensuring compatibility and maintaining operational reliability during the transition are critical, requiring skilled expertise and robust testing.
Balancing Technology Integration with Environmental and Safety Considerations
Implementing new technologies must be balanced with environmental and safety concerns:
- Environmental Impact: New infrastructure and technologies can have significant environmental impacts, both positive and negative. Ports need to consider emissions, waste management, and ecosystem disruption. Implementing green technologies and sustainable practices can mitigate some of these impacts but often at a higher initial cost.
- Safety Standards: Introducing new machinery and automated systems can raise safety issues, particularly during the transitional phase when human workers and automated systems must interact. Ensuring safety involves rigorous training, constant monitoring, and sometimes a complete overhaul of safety protocols.
- Community Relations: Ports are often located near urban areas, and changes in operation can affect local communities. Issues such as increased traffic, noise, and pollution need careful management to maintain good relations and avoid community pushback.
- Long-Term Viability: Technology evolves rapidly, and investments in certain technologies can become obsolete within a few years. Ports must choose solutions that not only meet current needs but are also adaptable to future developments.
- Cybersecurity Risks: With increased digitization, ports become more vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Protecting digital infrastructure and ensuring the security of data and operational systems is crucial.
Future Trends and Predictions
Emerging Technologies Likely to Influence Port Operations and Turnaround Times
- Blockchain Technology: By creating transparent and secure digital ledgers, blockchain can streamline operations such as contract management, customs clearance, and cargo tracking. This will further reduce delays and enhance security in port operations.
- 5G and Advanced Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will enable faster and more reliable data transfer, enhancing communication between port operations, shipping lines, and logistics providers. This connectivity will support other technologies like IoT and AI, making port operations even more efficient.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI can predict equipment failures, optimize cargo loading patterns, and automate routine decisions, reducing human error and increasing operation speed. Machine learning algorithms can analyze historical data to optimize scheduling and resource allocation.
- Autonomous Vehicles and Vessels: Self-driving cargo trucks and autonomous ships could revolutionize logistics by enabling continuous, 24/7 operations, reducing labor costs, and enhancing safety.
Predictions on the Future Landscape of Maritime Logistics with Advancing Port Technologies
The integration of advanced technologies in ports is likely to lead to a more connected and efficient global supply chain. We can expect:
- Shorter and More Predictable Turnaround Times: Enhanced efficiency and streamlined processes will reduce delays and variability in ship schedules.
- Increased Port Capacity and Throughput: Automation and better resource management will allow ports to handle more cargo without needing proportional increases in space or personnel.
- Greater Sustainability: Advances in technology will enable ports to reduce their carbon footprint and minimize environmental impact, aligning with global sustainability goals.
- Enhanced Global Trade Efficiency: As ports become more efficient, the overall cost of maritime transport will decrease, making goods cheaper and more accessible worldwide.
Continual improvement in port infrastructure is not just beneficial; it’s necessary for the sustainability and growth of the maritime industry. As global trade continues to expand and environmental regulations become stricter, ports must adapt to remain competitive and effective. The integration of advanced technologies will play a critical role in this evolution, promising a future where maritime logistics are faster, safer, and more environmentally friendly than ever before.

Do you have any feedback or additional insights? Please reach out to editor @ shipuniverse.com



