From Data to Decisions: Leveraging IoT for Optimized Fleet Performance

The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a revolutionary force, transforming how industries operate by connecting physical devices to the digital world. This network of interconnected devices collects and exchanges data, enabling more efficient, automated, and insightful decision-making. From smart homes to advanced manufacturing, IoT’s impact is vast and far-reaching, driving innovation and optimizing processes across various sectors.
* Please send feedback/suggestions to editor @ shipuniverse.com
Relevance to Ship Owners
For ship owners, IoT technology presents a unique opportunity to revolutionize fleet management. The maritime industry, with its complex operations and substantial costs, can greatly benefit from the real-time data and automation that IoT provides. By leveraging IoT, ship owners can enhance operational efficiency, improve safety, reduce fuel consumption, and ensure compliance with stringent environmental regulations. The ability to monitor vessels in real-time and predict maintenance needs can prevent costly downtime and extend the lifespan of valuable assets. Additionally, IoT helps streamline communication and coordination across fleets, leading to more efficient and effective operations.
Overview of the Key Points
This discussion will explore the transformative potential of IoT in maritime fleet management, covering several critical aspects:
- Understanding IoT in Fleet Management
- A clear definition of IoT and its specific applications within the maritime industry.
- Enhancing Operational Efficiency with IoT
- The benefits of real-time monitoring for ship operations.
- How data analytics provide actionable insights.
- The role of automation in reducing manual workload and errors.
- Improving Safety and Compliance
- Methods for monitoring vessel integrity.
- Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations through IoT.
- Enhancing crew safety and welfare with innovative IoT applications.
- Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
- Strategies for optimizing fuel management to cut costs.
- Predictive maintenance and its role in preventing unexpected breakdowns.
- Challenges in Implementing IoT in Fleet Management
- Addressing technical challenges and finding practical solutions.
- Initial investment costs versus long-term return on investment.
- Navigating regulatory and compliance issues effectively.
- Future Trends and Innovations
- Anticipated advancements in IoT technology.
- Real-life case studies demonstrating successful IoT implementation in the maritime sector.
Through these key points, ship owners will gain a comprehensive understanding of how IoT can revolutionize fleet management, providing practical insights and examples to guide the adoption of this innovative technology.
Understanding IoT in Fleet Management
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that communicate with each other and exchange data over the internet. These devices, equipped with sensors and software, collect and transmit data, allowing for real-time monitoring, control, and automation. The basic components of IoT include:
- Sensors and Devices: These gather data from the physical environment. For example, temperature sensors, GPS trackers, and fuel monitors.
- Connectivity: This enables the devices to communicate with each other and with central systems, typically through the internet or other communication networks.
- Data Processing: This involves analyzing the collected data to generate meaningful insights. This can be done locally on the devices or remotely in the cloud.
- User Interface: This allows users to interact with the system, view data, and make decisions. This could be a dashboard on a computer or an app on a mobile device.
IoT in Maritime Context
In the maritime industry, IoT plays a crucial role in enhancing fleet management by integrating advanced technologies to monitor and manage various aspects of ship operations. Here’s how IoT applies specifically to maritime fleet management:
- Real-Time Monitoring: IoT devices on ships continuously monitor key parameters such as fuel consumption, engine performance, hull integrity, and environmental conditions. This data is transmitted in real-time to central systems where it is analyzed to provide insights into the vessel’s operational status.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing data from various sensors, IoT systems can predict potential equipment failures before they occur. This allows for timely maintenance and repairs, reducing downtime and preventing costly breakdowns.
- Route Optimization: IoT technology helps in optimizing navigation routes based on real-time data such as weather conditions, sea currents, and traffic. This leads to more efficient fuel usage and shorter travel times.
- Environmental Compliance: IoT sensors monitor emissions and other environmental factors, ensuring ships comply with international regulations. This is crucial for avoiding fines and maintaining a sustainable operation.
- Crew Safety and Welfare: Wearable IoT devices can monitor crew health and safety conditions, providing alerts in case of emergencies. This ensures better health management and quick response to potential hazards.
- Cargo Management: IoT enables real-time tracking of cargo conditions, ensuring that goods are transported under optimal conditions. This is especially important for perishable goods and other sensitive cargo.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency with IoT
Real-Time Monitoring
IoT devices enable real-time monitoring of ship operations by collecting and transmitting data continuously. These devices are equipped with various sensors that measure and report on key operational parameters. Some examples of parameters monitored include:
- Fuel Consumption: Sensors track how much fuel is being used at any given time, helping to identify inefficiencies and optimize usage.
- Engine Performance: IoT devices monitor engine conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and vibration, ensuring that engines operate within optimal parameters and identifying potential issues before they lead to breakdowns.
- Navigation Routes: GPS and other location-based sensors provide real-time tracking of the vessel’s position, allowing for better route planning and adjustments based on current conditions.
By having access to this real-time data, ship owners and operators can make immediate adjustments to improve efficiency, reduce fuel costs, and ensure that the ship is operating safely and effectively.
Data Analytics and Insights
The data collected from IoT devices is not just accumulated but analyzed to provide actionable insights. Advanced data analytics platforms process the vast amounts of data generated by IoT sensors, transforming it into meaningful information that can guide decision-making. The benefits of data-driven decision-making include:
- Operational Optimization: By analyzing data patterns, ship operators can identify trends and anomalies, optimizing operations for better performance.
- Predictive Maintenance: Data analytics can predict when maintenance is needed, based on real-time conditions rather than fixed schedules. This approach reduces downtime and extends the lifespan of equipment.
- Resource Allocation: Insights from data analytics help in better resource allocation, ensuring that fuel, crew, and cargo are managed efficiently.
Data-driven decision-making allows ship owners to move from reactive to proactive management, addressing issues before they become problems and continuously improving operational performance.
Automated Systems and Processes
IoT technology also plays a crucial role in automating various processes on ships, which reduces the manual workload and minimizes human error. Automation driven by IoT includes:
- Automated Cargo Management: IoT systems can manage cargo loading and unloading processes, ensuring that weight distribution is optimal and that goods are handled efficiently. This reduces the time spent in port and enhances the overall logistics of shipping operations.
- Route Optimization: IoT-enabled navigation systems can automatically adjust routes based on real-time data such as weather conditions, sea currents, and traffic. This ensures that ships take the most efficient paths, saving fuel and reducing travel time.
These automated systems streamline operations, allowing the crew to focus on more critical tasks and ensuring that the ship operates at peak efficiency. The reduction in manual intervention also decreases the likelihood of errors, enhancing overall safety and reliability.
Improving Safety and Compliance
Vessel Integrity Monitoring
IoT sensors play a crucial role in monitoring the structural health of vessels, ensuring that potential issues are detected early and addressed promptly. These sensors continuously collect data on various aspects of the ship’s integrity, providing real-time insights into its condition. Examples include:
- Hull Integrity: Sensors placed along the hull of the ship monitor for signs of stress, corrosion, and other structural weaknesses. By detecting anomalies early, preventive maintenance can be performed, avoiding costly and dangerous failures.
- Engine Health: IoT devices track engine parameters such as temperature, pressure, and vibration levels. Any deviation from normal operating conditions can indicate potential problems, allowing for timely interventions to prevent engine failures.
By leveraging IoT technology for vessel integrity monitoring, ship owners can maintain their fleets in optimal condition, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and enhancing overall safety.
Environmental Monitoring
Compliance with environmental regulations is a critical concern for the maritime industry. IoT helps in monitoring environmental conditions, ensuring that ships adhere to international standards and avoid penalties. Key areas of focus include:
- Emission Levels: IoT sensors measure emissions from the ship’s engines and other systems. Real-time monitoring ensures that emission levels stay within regulatory limits, helping to minimize the vessel’s environmental footprint and comply with laws such as the IMO 2020 sulfur cap.
- Ballast Water Quality: IoT devices monitor the quality of ballast water, ensuring that it meets the required standards before being discharged. This prevents the spread of invasive species and protects marine ecosystems.
With IoT-driven environmental monitoring, ship owners can ensure compliance with stringent regulations, contributing to sustainable maritime operations and avoiding fines and sanctions.
Crew Safety and Welfare
The safety and welfare of the crew are paramount in maritime operations. IoT applications enhance crew safety and welfare through various innovative solutions, including:
- Wearable Devices for Health Monitoring: Crew members can wear IoT-enabled health monitoring devices that track vital signs such as heart rate, temperature, and physical activity. These devices can alert medical personnel to any health issues in real-time, allowing for immediate intervention.
- Communication Systems for Emergency Situations: IoT-powered communication systems ensure that crew members can stay connected at all times, especially in emergencies. These systems provide real-time updates and enable quick coordination, improving response times and overall safety.
By integrating IoT technologies to monitor and enhance crew safety and welfare, ship owners can create a safer and more supportive working environment. This not only protects the crew but also boosts morale and productivity, contributing to smoother and more efficient operations.
Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
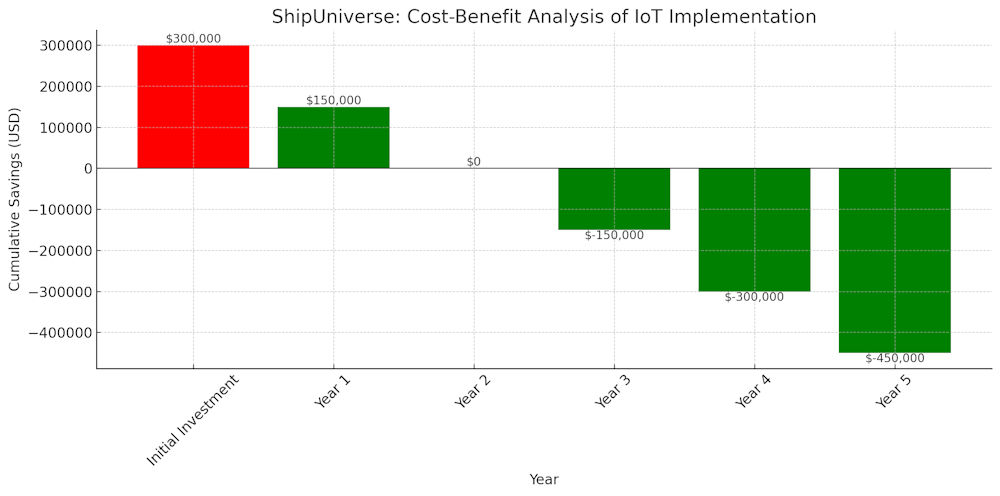
Real-World Data Points (for chart context):
- Fuel Savings: A study by the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) reported potential fuel savings of up to 10-20% through IoT and data analytics.
- Maintenance Cost Reduction: Companies implementing predictive maintenance solutions often report up to 20-30% reductions in maintenance costs.
- Downtime Reduction: Real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance can reduce downtime by 30-50%.
Fuel Management
IoT solutions play a pivotal role in optimizing fuel consumption, which directly translates into significant cost savings for ship owners. By using a network of sensors and advanced analytics, IoT systems provide real-time data on fuel usage, enabling more efficient management and decision-making.
- Optimization through Real-Time Monitoring: IoT devices continuously monitor fuel consumption, engine performance, and navigation conditions. This data allows for real-time adjustments to speed, route, and engine settings, ensuring that fuel is used as efficiently as possible. For instance, by optimizing the vessel’s speed according to sea conditions and traffic, fuel efficiency can be significantly improved.
- Predictive Analytics: By analyzing historical and real-time data, IoT systems can predict the most fuel-efficient routes and speeds, further reducing unnecessary fuel consumption.
Case Study Example: A shipping company implemented IoT-based fuel management systems across its fleet. Sensors were installed on each vessel to monitor fuel consumption, engine performance, and environmental conditions. The data collected was analyzed to identify patterns and inefficiencies. Through real-time adjustments and optimized routing, the company achieved a 15% reduction in fuel consumption within the first year, resulting in substantial cost savings and a lower environmental impact.
Maintenance and Repairs
Predictive maintenance, enabled by IoT technology, is another critical area where cost reduction and resource optimization are achieved. Traditional maintenance schedules are based on fixed intervals, which often lead to either unnecessary maintenance or unexpected breakdowns. IoT shifts this paradigm by using real-time data to schedule maintenance only when it is truly needed.
- Real-Time Data Collection: IoT sensors continuously monitor the condition of critical components such as engines, pumps, and hull structures. Parameters like temperature, vibration, and pressure are tracked to detect any deviations from normal operating conditions.
- Predictive Maintenance: The collected data is analyzed to predict when a component is likely to fail or require maintenance. This approach allows for maintenance activities to be scheduled based on actual wear and tear rather than arbitrary timelines, preventing unexpected breakdowns and minimizing downtime.
Example: A cargo ship equipped with IoT sensors for engine monitoring experienced fewer breakdowns after implementing predictive maintenance. The IoT system detected early signs of wear in the engine’s cooling system, which would not have been apparent during regular inspections. Maintenance was scheduled proactively, preventing a potential failure that could have resulted in significant repair costs and operational delays. As a result, the ship maintained a higher operational efficiency and reduced overall maintenance expenses by 20%.
Challenges in Implementing IoT in Fleet Management
Technical Challenges
Integrating IoT systems on ships comes with several technical challenges that need to be addressed to ensure successful implementation.
- Connectivity Issues: One of the primary challenges is maintaining reliable connectivity at sea. Ships often travel through remote areas with limited or no internet access, making continuous data transmission difficult. Solutions like satellite communication systems can provide connectivity, but they can be expensive and have latency issues.
- Data Security Concerns: With the increased use of IoT devices, data security becomes a significant concern. Ships generate and transmit vast amounts of sensitive data, including operational parameters and navigation routes. Ensuring this data is secure from cyber threats is crucial. Implementing robust encryption, secure communication protocols, and regular security audits are necessary to protect against cyberattacks.
Cost and Investment
The initial costs and investments required for IoT implementation can be substantial, which can be a barrier for many ship owners.
- Initial Investment: Setting up an IoT infrastructure involves purchasing and installing sensors, upgrading communication systems, and integrating data analytics platforms. These costs can add up quickly, especially for larger fleets.
- Long-term ROI Considerations: While the upfront costs can be high, the long-term return on investment (ROI) is a crucial consideration. IoT systems can lead to significant cost savings through optimized fuel consumption, reduced maintenance costs, and improved operational efficiency. For example, predictive maintenance can prevent expensive repairs and downtime, while real-time monitoring can enhance fuel efficiency and reduce operational costs. Ship owners should consider these long-term benefits and potential cost savings when evaluating the initial investment in IoT technology.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Navigating the regulatory landscape is another challenge in implementing IoT in fleet management. Ship owners must ensure their IoT systems comply with various international standards and regulations.
- Regulatory Challenges: Different countries and regions have their own regulations regarding data privacy, environmental standards, and maritime operations. Ensuring that IoT systems comply with these diverse regulations can be complex and time-consuming.
- Need for Compliance with International Standards: Compliance with international standards such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations is essential. For example, the IMO’s 2020 sulfur cap regulation requires ships to monitor and report their sulfur emissions accurately. IoT systems can help in meeting these compliance requirements by providing real-time data on emissions and other environmental factors. However, staying updated with evolving regulations and ensuring continuous compliance can be challenging.
Future Trends and Innovations
Advancements in IoT Technology
The maritime industry is poised to benefit from several exciting advancements in IoT technology. These innovations promise to further enhance efficiency, safety, and sustainability in fleet management.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: The integration of AI with IoT systems can lead to more sophisticated data analytics and predictive capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze complex datasets from IoT sensors to identify patterns and make more accurate predictions about maintenance needs, fuel optimization, and route planning.
- Enhanced Connectivity Solutions: The development of advanced connectivity solutions, such as 5G and low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite networks, will address the connectivity challenges at sea. These technologies will provide more reliable and faster internet connections, enabling continuous data transmission and real-time monitoring even in remote ocean areas.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage, allowing for faster decision-making and more efficient operations. For ships, edge computing can mean quicker responses to sensor data and more immediate adjustments to operations.
- Advanced Environmental Monitoring: New IoT sensors are being developed to provide more accurate and comprehensive environmental monitoring. These sensors can detect a wider range of pollutants and environmental conditions, helping ships comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
- Blockchain Technology: Integrating blockchain with IoT can enhance security and transparency in maritime operations. Blockchain can ensure the integrity of data collected from IoT devices, making it tamper-proof and reliable for regulatory compliance and operational audits.
Case Studies of Successful IoT Implementation
Real-life examples of successful IoT implementation in the maritime industry provide valuable insights and inspiration for ship owners considering this technology.
- Smart Ports: Ports like the Port of Rotterdam have implemented IoT systems to optimize logistics and reduce turnaround times. IoT sensors track cargo movements, monitor equipment status, and manage port traffic, leading to more efficient and sustainable operations.
- Autonomous Ships: Companies like Rolls-Royce and Wärtsilä are developing autonomous ships equipped with IoT and AI technologies. These vessels can navigate and operate with minimal human intervention, using IoT data to make real-time decisions and improve safety.
The integration of IoT in fleet management offers ship owners a transformative opportunity to enhance efficiency, safety, and sustainability. By leveraging real-time monitoring, data analytics, and automation, IoT technology can optimize operations, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
While there are challenges to implementing IoT, such as connectivity issues, data security concerns, and initial investment costs, the long-term benefits far outweigh these obstacles. The advancements in IoT technology, including AI integration, enhanced connectivity, edge computing, and blockchain, promise to further revolutionize the maritime industry.
Ship owners who embrace IoT will be better positioned to navigate the complexities of modern maritime operations, achieving greater operational efficiency, improved safety, and reduced environmental impact. The future of fleet management lies in the intelligent use of IoT technology, paving the way for a more connected and efficient maritime industry.

Do you have any feedback or additional insights? Please reach out to editor @ shipuniverse.com

